| |
DSZV-EP
|

|
| DIGITAL LONGITUDINAL DIFFERENTIAL
PROTECTION |
| |
| The digital longitudinal differential protection
of type DSZV-EP is part of device family named EuroProt. This short description
contains special data of this type. General and common features of EuroProt
family can be found in the EuroProt system information sheet. Accordingly
it is proposed to study both this short description and system information
sheet too, in order to understand the device entirely. |
| |
|
| |
| Application |
| |
| The DSZV-EP three phase digital longitudinal
differential protection with phase current comparison may be applied to
a selective instantaneous short-circuit protection of high voltage transmission
lines or cables. The protection needs an optical fibre cable interconnection
between the two ends. The protection is also able to serve alone a short-circuit
protection of a transmission line or cable which includes a transformer
in block. |
| |
| Main features |
| |
- Current instantaneous value comparison in each phase
- Optical fibre cable interconnection between the two ends
- Continuous watching the soundness of main optical fibre cable
- Trip given per phase
- Trip may be blocked by current and/or voltage condition
- One side (master) device controls the counter side (slave) device
to get samples in the identical moment on both sides
- Characteristic of three sections settable in details arbitrary
- Protection not only to the line or cable but together with a transformer
in block
- No additional matching auxiliary C.T.'s to adjust either the C.T.
ratios, or the vector rotation due to the transformer connection group
- Bias by the average of the two side currents
- Insensitive against transformer inrush current
- Operation time about 25 to 35 ms
- Failure annunciation with phase conformity
- Overcurrent relay built in the protection as well
- Continuous "ready-to-work" self-check monitoring system
- 16 output relays controlled by a programmable software matrix
- Event log with 50 events and digital event sequence recorder with
300 events of 1 ms resolution
- Communication channel through series RS 232 connector or optical fibre
cable
- 8 digital inputs with optical couplers, seven of which give external
arbitrary information's to the counter side of line through the main
optical fibre cable, and one of which is an input for clock synchronising
- Seven external arbitrary information's through the main optical fibre
cable from the counter side actuate output relays here according to
the software matrix programming
- Real time clock handling by the aid of a RAM with battery
- Clock synchronisation by an external PC, or by a local area transmitter
through digital optical coupler input by the aid of a World Time Synchroniser
(WTS) made by PROTECTA Electronics Co.Ltd.
- As an option, an independent disturbance recorder PCB of DIGIPROT
disturbance recorder family may also be built in the device which can
record the currents and voltages of the line as analogue signals as
well as digital signals characterised the protection operation, and
it is able to store a period of 50, 100 or 150 s as a sum.
|
| Working principle |
| |
| The analogue current and voltage inputs are
led through auxiliary measuring transformers and analogue low pass filters
to a multiplexer, sample-and-hold circuit and A/D converter. The protection
evaluates by comparison of current instantaneous values in three phases
whether the short circuit is an inner fault, so the protection has to trip
or an external fault and so the protection has to block. 10 instantaneous
values after one another are compared, then after one cycle, in a following
window, it is repeated and if the evaluation indicates difference twice
after one another, the protection trips. To get samples in the identical
moment, the protection on one side is a master device on the counter side
is a slave device. The master device gives a synchronising signal through
the [main] optical fibre cable to the counter side where the slave device
receives it. So the software of the two devices is not the same it is marked
on the device by master or slave inscriptions which are written on the left
side hand lever of the protection, perpendicularly.
Due to the C.T. transfer failure the protection has to work with a bias
characteristic (see Figure 1).
The protection communicates with the counter side through a [main] optical
fibre cable suitable safely installed. An optical fibre cable may be realisable
e.g. put in an earth wire but it is also possible to lay under ground,
to put to auxiliary arms mounted to the transmission line towns, or optical
fibre cable installing on other safe mode for interconnection.
Against false trip of a longitudinal differential protection, it is advisable
to actuate the overcurrent and/or the voltage condition in the protection.
The protection does not need additional matching auxiliary C.T.'s to
adjust the main C.T. ratios for balancing, but the currents on both sides
has to be set properly.
If a transformer is connected in block with the transmission line or
cable, the current settings are made for balancing taking the transformer
also into account, and the vector rotation has to be set in the protection
to match the transformer connection group (e.g.Yd11). The protection is
insensitive to the transformer inrush current if it is set.
The tripping characteristics of the DSZV-EP longitudinal differential
protection is shown in Figure 1.
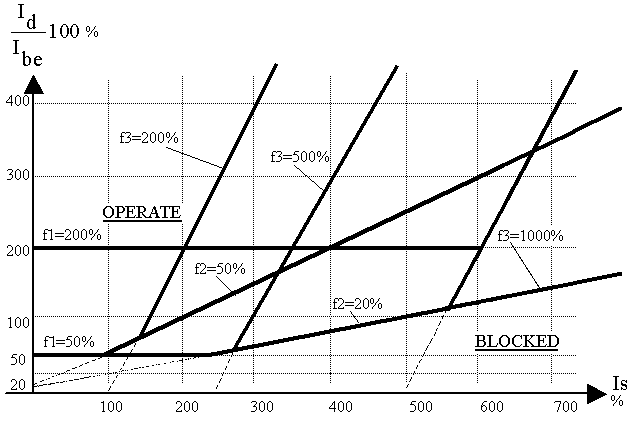
Figure 1.
Separate sections of the tripping characteristics have meanings as follows.
f1% Setting of the first, horizontal section of a characteristic. It
determines the basic sensitivity of longitudinal differential protection
in per cent of rated current set.
f2% Setting of second section incline of the characteristic. It is necessary
to compensate the different features between the own side C.T. group and
the counter side C.T. group in overcurrent range, and the regulating range
of transformer eventually inserted, since the protection is balanced to
the middle position, so a regulation shifts it. This section is a line
originated from the origin.
f3% Setting of the third section. It is necessary to compensate the C.T.
saturation, so its gradient is always tga=2, and originating on the vertical
axis at [-f3%]
f2h Setting of the second harmonic blocking. It is necessary against
false trip on inrush current of the transformer eventually inserted. It
blocks the trip if the second harmonic content of the differential current
in per cent is more then the set value. If no transformer inserted f2h
= 100% is to be set.
Id>> Setting of a high current value. If the differential current
is higher than the set one the protection trip without bias. Then the
operation time is shorter (15 to 20 ms).
The function signal information's of the longitudinal differential protection
are transfer through an optical fibre cable between the two sides of the
protected line. Through this main optical cable, seven yes-not signals
of other aim may be transferred as well. The signal inputs and outputs
are entirely independent of the longitudinal differential protection functions.
The transfer time is about 7 to 10 ms taking also the digital filters
into account.
The protection has 8 output relays which may be programmed by software
matrix. It means each output relay has an own number (2nd code number)
and if this number is written after one of unit signs (e.g. differential
relay trip, overcurrent relay trip, etc.), the output relay will be actuated
by it.
|
| |
| Technical data |
| |
| Rated secondary current, In |
1 A or 5 A |
Rated secondary voltage, Un
|
100 V or 200 V |
Overload capacity, thermal, continuous
1 s |
4×In
100×In (if In = 1 A)
50×In (if In = 5 A) |
|
|
|
| Dynamic current limit |
100×In |
| Accuracy, digital voltage relay |
± 2 % |
| Accuracy, digital overcurrent relay (over 50 %) |
± 2 % |
Accuracy, digital time delaying: 10 ms
1 s |
± 3 ms
± 12 ms |
|
| Resetting ratio, voltage and overcurrent relay |
95 % |
| Operating time, with signal transfer time |
30 ± 5 s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of output contacts (programmable with digital
matrix) |
16 pcs print relays |
|
Output contacts, electrical data:
rated switching voltage
continuous load current
making current
DC breaking capability at 220 V,
at pure conductive load
at load of L/R = 40 ms
at load of L/R = 40 ms (optionally)
|
250 V
8 A
16 A
0.25 A
0.14 A
4 A |
| Auxiliary DC voltage |
220 V or 110 V (range: 88 V to 310 V) |
| Permissible ambient temperature |
0°C to 50°C |
|
|
| Insulation test (IEC 255) |
2 kV, 50 Hz
5 kV, 1.2/50 ms |
|
| Disturbance test (IEC 255) |
2.5 kV, 1 MHz |
| Electrostatic discharge (ESD, IEC 801-2) |
8 kV |
|
| BURST test (IEC 801-4) |
2 kV |
| Setting ranges: |
|
| Main C.T.'s, primary rated currents |
50 to 1500 A, step 25 A |
| Overcurrent relay, starting value, I>/IAV |
50 to 2500 %, step 5 % |
| Line or transf.rated current on own side, Ibe[own] |
20 to 270 %, step 2 % |
| The same but on the counter side, Ibe[counter] |
20 to 270 %, step 2 % |
| Trip blocking voltage condition, U>/Un
[Ucond] |
20 to 100 %, step 5 % |
| Longitudinal diff. protection basic sensitivity, f1 |
50 to 200 %, step 2 % |
| Characteristic, second section incline, f2 |
40 to 80 %, step 2 % |
| Characteristic, third section incline, f3 |
200 to 2000 %, step 10 % |
| Inrush current block, second harmonic factor, f2h |
10 to 100 %, step 2 % |
| Transformer angle rotation (hour angle) |
[0-11] code sign |
| Overcurrent relay time delaying, t[I>] ms |
0 to 60000 ms, step 10 ms |
| Main optical fibre cable failure signal, time delaying |
0 to 60000 ms, step 10 ms |
| "Ready-to-work" check time delaying |
fixed 5 s |
| External communication channel |
RS 232 or optical fibre cable |
| Communication rate (Baud Rate) |
150 to 19200 Baud (2× step) |
| No. of substations within a system |
0 to 254 |
| No. of devices within a substation |
0 to 254 |
|
| |
| Design, size |
| |
| The device is a member of the family EuroProt
which has two different designs. The one is a device for rack mounting to
a 19" standard cabinet frame, the other is a flash mounting or raising
mounting device to a panel. Its size depends, of course, on the design chosen. |
| |
|
Design
|
Width
|
Height
|
Depth
|
|
Rack mounting
|
483 mm
|
132,5 mm
|
201 mm
|
|
Panel mounting
|
384 mm
|
250 mm
|
250 mm
|
|
| |
| Options |
| |
- Disturbance recorder
- Interface to a SCADA system
- Output sontatcs with 4 A DC breaking capability
|
| |
| Information required with order |
| |
- Type of protection [DSZV-EP]
- Rated current [1 A, 5 A]
- Rated voltage [100 V, 200 V]
- Auxiliary d.c. voltage [220 V, 110 V]
- Options [if needed]
|
|
|